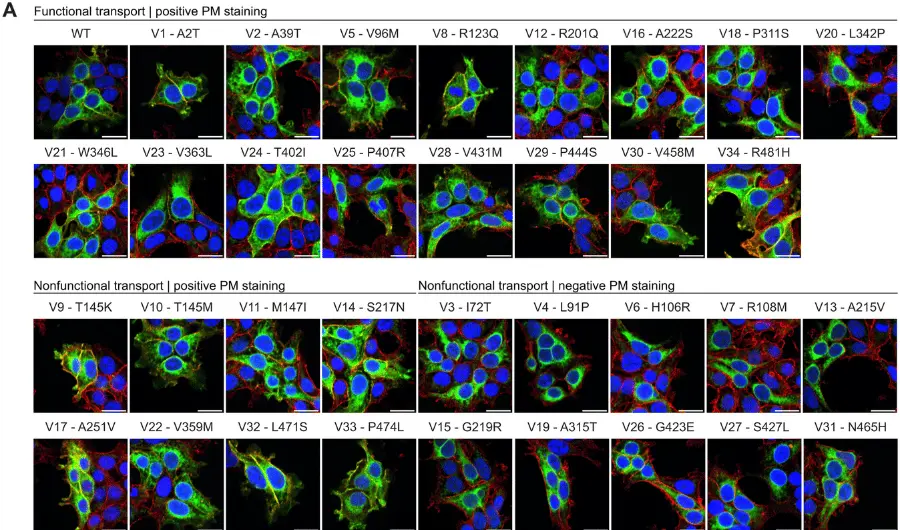
The Epidemiology of Epilepsy in Older Adults: A Narrative Review by the ILAE Task Force on Epilepsy in the Elderly
February 3, 2023
Abstract found on PubMed
In an aging world, it is important to know the burden of epilepsy affecting populations of older persons. We performed a selective review of epidemiological studies that we considered to be most informative, trying to include data from all parts of the world. We emphasized primary reports rather than review articles. We reviewed studies reporting the incidence and prevalence of epilepsy that focused on an older population as well as studies that included a wider age range if older persons were tabulated as a subgroup. There is strong evidence that persons older than approximately 60?years incur an increasing risk of both acute symptomatic seizures and epilepsy. In wealthier countries, the incidence of epilepsy increases sharply after age 60 or 65?years. This phenomenon was not always observed among reports from populations with lower socioeconomic status. This discrepancy may reflect differences in etiologies, methods of ascertainment, or distribution of ages; this is an area for more research. We identified other areas for which there are inadequate data. Incidence data are scarcer than prevalence data and are missing for large areas of the world. Prevalence is lower than would be expected from cumulative incidence, possibly because of remissions, excess mortality, or misdiagnosis of acute symptomatic seizures as epilepsy. Segmentation by age, frailty, and comorbidities is desirable, because “epilepsy in the elderly” is otherwise too broad a concept. Data are needed on rates of status epilepticus and drug-resistant epilepsy using the newer definitions. Many more data are needed from low-income populations and from developing countries. Greater awareness of the high rates of seizures among older adults should lead to more focused diagnostic efforts for individuals. Accurate data on epilepsy among older adults should drive proper allocation of treatments for individuals and resources for societies.